- General Scenario and Current Trend : Total geographical area of the state is 22.2 lakh sq. kms having 7.52 lakh ha of Net Sown Area. A large part of the state forms part of the Himalayan Mountains. The state is geologically constituted of rocks varying from the oldest period of the earth?s history to the youngest present day river and lake deposits. The climate varies from tropical in Jammu to temperate in Kashmir valley and in Jammu mountain tracts to semi-arid cold climatic conditions in Ladakh. There is a sharp rise of altitude from 1000 ft to 28250 ft above mean sea level within state?s four degrees of latitude. There are different kinds of soil exists in state which has soil deficiency. The problem of various kinds of erosion also exists.
Average annual rainfall is 619 mm which ranges from 92.6 mm in Ladakh to 650.5 mm in Kashmir to 1115.9 mm in Jammu. Net Irrigated Area is 3.11 lakh ha which is 42% of Net Sown Area.
85% of the farmer is small and marginal and the average size of holding is 0.66 ha.
Seed planning, production, SRR, SMR and VRR are areas to be addressed immediately. SRR has been achieved only in paddy (Kharif). SMR has not been achieved in any crop by the state. Production and productivity of maize is increasing but area under kharif paddy is decreasing.
As per the 3rd Advance Estimates of 2008-09, productivity of rice is 2143 kg/ha, wheat 1839 kg/ha, jowar 310 kg/ha, bajra 589 kg/ha, maize 1480 kg/ha, total pulses 500 kg/ha and total oilseeds 622 kg/ha.
An area of 1.94 lakh ha area is under fruit cultivation and productivity of fruits is 7.4 MT/ha. Vegetable is grown in 58,553 ha of area having productivity of 21.1 MT/ha. 33,000 ha area is under flower cultivation. 63.3% of total apple production of the country is from J&K.
Agriculture and allied sector contributes appox 25% to its GSDP
-
Strength: 4 agro-climatic zones, diverse bio-diversity.
-
Limitation: Mostly hilly, soil erosion, mining, lack of connectivity, inadequate marketing infrastructure, limitation of irrigation, single cropping in high altitude areas. State has to import food grain, meat, egg from outside the state to fulfill its requirement. There is deficiency of 5 lakh MT of food grains, 70% of oilseed and pulses requirement and 30% of vegetable requirement.
- Public Investment : In recent years, the state has made a few interventions in agriculture and allied
sector to increase productivity through State Plan resources as well as through centrally sponsored schemes
assistance from GOI. In the year 2005-06, out of Rs.3555.62 cr State Plan, agriculture and allied sector
received Rs.305.65 cr (8.60%). In 2006-07 this sector received Rs.218.77 cr (6.15%) out of Rs.3555.61 cr
State Plan and in 2007-08, Rs.104.12 cr (2.15%) out of Rs.4850 cr State Plan was provided for the sector. In
2008-09, Rs.177.32 cr (3.22%) was provided in the agriculture & allied sector.
During 2007-08, Ministry of Agriculture & Cooperation, Government of India, allocated Rs.42.40 cr, Rs.1.5 cr under ISOPOM, Rs.6.85 cr under RKVY, Rs.24.00 cr under TMNE (Horticulture).
During 2008-09, Rs.24.00 cr under TMNE (Horticulture), Rs.16.17 cr under RKVY, Rs.0.75 cr under ISOPOM and Rs.36.60 cr under MMA was provided.
Thus,in the last two years of 11th Plan period, Ministry of Agriculture, Government Of India allocated more than Rs.155 cr and State Government utilized Rs.281.44 cr from its State Plan resources for agriculture and allied sectors. The allocation from GOI could have been much more, but for low utilization of resources in the state.

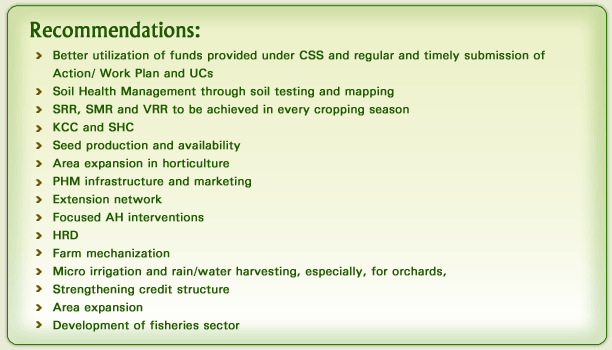
STATE HAS AGREED TO PREPARE TIME BOUND ACTION PLAN FOR THE STRATEGY AND RECOMMENDATION..